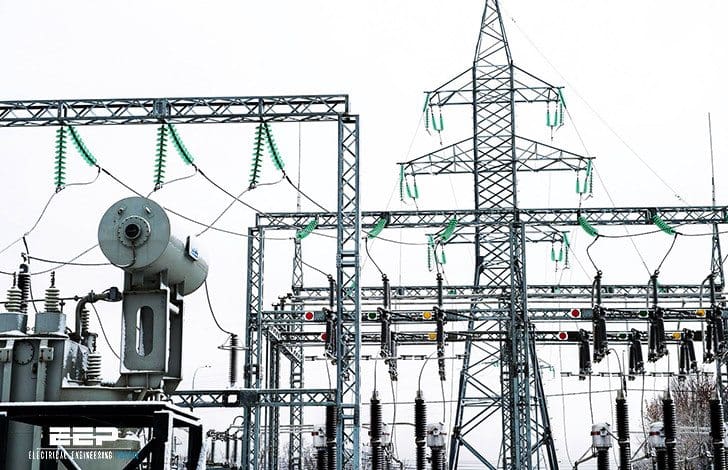
Substation role in the power system
An electrical substation is a part of an electricity generation, transmission and distribution system where voltage is transformed from high to low or in reverse using transformers. It also serves as a point of connection between various power system elements such as transmission lines, transformers, generators and loads.
To allow for flexibility in connecting the elements, circuit breakers are used as high power switches.
Electric power may flow through several substations between generating plant and consumer, and may be changed in voltage in several steps.
There are different kinds of substation such as Transmission substation, distribution substation, collector substation, switching substation and some other types of substation.
The general functions of a substation may include:
- Voltage transformation
- Connection point for transmission lines
- Switchyard for network configuration
- Monitoring point for control center
- Protection of power lines and apparatus
- Communication with other substations and regional control center
General criteria for substation design
For the substation development to reach its technical and economical potentials, the focus has moved now to studying how substations may enable more intelligence in the network, which is labeled the “smart grid” development.
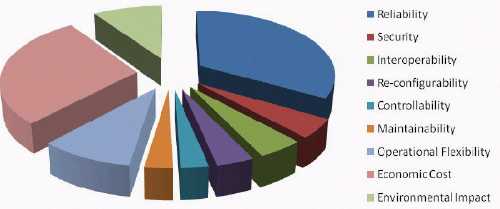
It has been concluded that the 21st century substation design should meet the following improved criteria: reliability, security, interoperability, re-configurability, controllability, maintainability, flexibility, reduced cost and environmental impact. An estimate of the importance of the different criteria is shown in Figure 1.










